what is a normal echo lvef Your health care professional might recommend one or more of these tests to measure your ejection fraction: 1. Echocardiogram(or “echo”) - the most widely used test 2. . See more At 9 projectiles, they are totally parallel with Greater Volley (gmp + gv) while they are not with regular volley (gmp + lmp + volley). How do the projectiles work at each projectile count when supported with greater volley? and both?
0 · left ventricular fraction normal range
1 · heart ejection fraction normal range
2 · echocardiogram numbers meaning
NIJ tested Level IV Armor will defeat 3 rifle round shots up to .30 Cal M2 AP @ 2887 ft/s @ 42 feet; 10×12 multi curved- set of 2 plates; Vest fits in all Green2 Vests; For front and/or back protection; Alumina; Covering: 600D nylon .
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal heart’s ejection . See moreAn EF from 41 to 49 percent might be considered too low. It does not always indicate that a person is developing heart failure, but it could indicate damage, perhaps from a previous heart attack. An ejection fraction measurement under 40 percent might be . See moreYour health care professional might recommend one or more of these tests to measure your ejection fraction: 1. Echocardiogram(or “echo”) - the most widely used test 2. . See moreYour health care professional might mention one of these two EF-related scenarios: 1. Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)– also . See more
What is a normal ejection fraction? Ejection fraction in a healthy heart is 50% to 70%. With each heartbeat, 50% to 70% of the blood in your left ventricle gets pumped out to your body. .
A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a sign of heart failure or an underlying heart.A normal ejection fraction of 55 to 65% is considered a sign of a healthy heart. People with an ejection fraction lower than 50% might be suffering from systolic heart failure. This is also termed Heart Failure with reduced ejection fraction. Thus, there is no clear range at which we can say the LVEF is normal (optimal health). For those enrolled in clinical trials (those without severe systemic disease), it appears that the higher the LVEF, the better the outcome. Ejection fraction is measured as a percentage of the total amount of blood in your heart that is pumped out with each heartbeat. A normal ejection fraction is 50 percent or higher. An ejection fraction below 40 percent means .
Things like time of day (biological cycles), eating (what and when), position (supine vs. upright), breathing, medications, etc. can all slightly change LVEF in a normal person. All of these factors make it . A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection . Normal ranges for two-dimensional echocardiography obtained LVEF as per the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging are: LVEF (%) among the male . The best method to define a normal LVEF, or any diagnostic test result, is unclear. Investigators tradi-tionally have evaluated populations who are assumed to be healthy .
priceline shower gel
LVEF is calculated from: LVEF: [SV/EDV] x 100 Normal ranges for two-dimensional echocardiography obtained LVEF as per the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging are: LVEF (%) among the male population: 52% to 72% normal range. 41% to 51 mildly abnormal. 30% to . Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) . Echocardiogram, or "echo." . A normal EF doesn't always mean your heart is healthy. You could have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle .
a depressed LVEF to persuade patients of the need for treatment. Therefore, patients often use any change in LVEF to track progress or deterioration in their condition. Although misguided, many patients will assume a report indicating a normal LVEF indicates recovery. Article, see p 732 The best method to define a normal LVEF, or any Your doctor can measure the ejection fraction using an echocardiogram (or "echo"), a normally painless procedure that outlines your heart’s movements using an ultrasound machine. . (LVEF) below normal. certain children 1 year of age and older with heart failure that causes symptoms. Entresto is a combination of two medicines: the neprilysin .LVEF should be derived from 2D volume data using the biplane Simpson’s method. Normal LVEF is defined as an EF ≥55%. Patients with an LVEF between 50 and 54% are defined as having ‘borderline low LVEF’. Patients with an LVEF between 36 and 49% are defined as having ‘impaired LVEF’.
Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) Definition. Ejection Fraction (EF) is a percentage of blood pumped by the LV with each contraction. Many factors can affect ejection fraction including preload, afterload, and contractility. A normal EF ranges from 55-69%, and is calculated using the following equation:
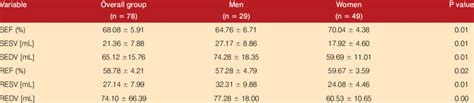
Echocardiogram: Regarded as the most efficient way to monitor ejection fraction over time, this non-invasive imaging test uses ultrasound to view the heart in motion.; Multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan: Also a non-invasive test, the MUGA scan is considered the most accurate and reproducible method of measuring ejection fraction.It typically is .A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. In Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography : official publication of the American Society of Echocardiography 30 (4), pp. 303–371. DOI: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.01.007. –>Pubmed-LinkNormal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women). Refer to Table 2 (normal values for non-contrast images) and Table 4 (recommendations for the normal range, mildly, moderately and severely abnormal ejection fraction). Below is an echocardiogram of a patient with a normal ejection fraction (EF= 55-60%). The stroke volume (SV) is calculated by taking the amount of blood estimated when the left ventricle is completely filled (end diastole= LVEDV = 131 ml) and subtracting the amount of blood remaining within the left ventricle when it is finished contracting .
For patients with impaired LVEF, GLS and LVEF have a linear relationship, with a GLS of −11% or −12% corresponding to an LVEF of 35%. 30,31 In contrast, GLS and LVEF have a curvilinear relationship in patients with normal LVEF. 31 Therefore, the ability of GLS to detect subclinical myocardial dysfunction is likely greatest for patients with .An ejection fraction (EF) is the volumetric fraction (or portion of the total) of fluid (usually blood) ejected from a chamber (usually the heart) with each contraction (or heartbeat).It can refer to the cardiac atrium, [1] ventricle, [2] gall bladder, [3] or leg veins, [4] although if unspecified it usually refers to the left ventricle of the heart. EF is widely used as a measure of the . 2. Be a heart detective. Put this on your doctor’s to-do list, too. By identifying and treating the underlying causes of low ejection fraction, you take major steps toward improving your quality .
left ventricular fraction normal range
heart ejection fraction normal range
European Society of Cardiology and American Society of Echocardiography guidelines report normal LVEF as >50% and >55%, respectively (2,3) and clinical HF trials have defined left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40-45% to indicate LV systolic dysfunction (4,5).Guidelines suggest that a normal or preserved LVEF is >50% , and as echocardiography reports of patients with an LVEF 50% to 55% commonly denote them as having “low-normal” LVEF, these patients may often be considered to have the same prognosis of patients with an LVEF of >55%. However, the authors show that this group is more likely to . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is a surrogate for left ventricular global systolic function, defined as the left ventricular stroke volume divided by the end-diastolic volume. Terminology Point-of-care echocardiography protocols typi.
A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.Normal values for LVEF, EDV, ESV, and stroke volume are shown in Table 1 . Determination of SV normally requires complex clinical methods such as echocardiography, oscillometry, computed .
Normal values for ejection fraction (EF) Studies in healthy individuals suggest that the mean ejection fraction is 63% to 69%. European and American guidelines concur that the lower normal limit for ejection fraction is 55%. Reduced ejection fraction is defined as ejection fraction <55%. classifications of heart failure using LVEF. Heart failure definition. Heart Failure with. Reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) - LVEF<40%; Mid-range ejection fraction (HFmEF) - LVEF 40- 49%; Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) - LVEF>=50%; Heart failure definition. Systolic impairment and EF. Severe reduction - EF <35%; Moderate reduction - EF 35-39%
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is one of the most commonly reported measures of left ventricular (LV) systolic function. It is the ratio of blood ejected during systole (stroke volume) to blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). If the LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volume (ESV) are known, LVEF can be . Impairment of left ventricular (LV) diastolic function is common amongst those with left heart disease and is associated with significant morbidity. Given that, in simple terms, the ventricle can only eject the volume with which it fills and that approximately one half of hospitalisations for heart failure (HF) are in those with normal/’preserved’ left ventricular .
The normal percentage of blood ejected from the heart is in the range of 50-70% depending on different factors. If the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is 45% (& that is not a measurement error), then it is mildly reduced. The list of possible reasons why is quite extensive & should be discussed with your doctor.Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr . Diastolic Function Assessment in the Presence of a Normal LVEF (Figure 8A) The presence or absence of diastolic dysfunction in patients with a normal LVEF is based on the assessment of four . However, LVEF is an imperfect measure of LV contractility, affected also by preload, afterload, heart rate, and LV geometry. LVEF can be measured using radionuclide imaging, contrast angiography, echocardiography, and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. Nuclear methods have poor temporal resolution, which can lead to underestimation .
LVEF is a continuous variable with a normal distribution within the general population—a distribution that changes with age and sex, thus challenging a single precise threshold for “normal.” Indeed, although HF guidelines used a cutoff of 50%, echocardiography guidelines used a threshold of 55% to define normal LVEF.
lv on the beach
Gribu LV COM piedāvā iespēju publicēt slidinājumus par brīvu un meklēt iespējas internetā. Nekādu izdevumu - reģistrējies tūlīt un publicē bez maksas!
what is a normal echo lvef|heart ejection fraction normal range